At a time when the younger generations are increasingly looking for meaning in their work, employee involvement and retention remains a top priority for company managers. Motivated and committed employees will always have a positive effect on the company’s results.
All means are good for keeping employees involved and motivated:
- Develop team spirit and a good working atmosphere
- Offering training courses
- Enable teleworking and promote a work-life balance
- Comfortable premises and a better working environment for employees (the Google method)
However, even if it remains taboo in France, one of the main motivations for employees is unquestionably financial. Beyond the salary, the idea of being financially involved in the company’s success is a leitmotif for many people, and even more so for the younger generation.
Forbes magazine had already pointed out this gap between France and the American system, where employees are prepared to make concessions on their remuneration in exchange for shares in the company’s capital.

Nevertheless, it would seem that the situation is changing with the rise of French start-ups in recent years. According to Les Echos, Blablacar has even generalized the distribution of shares, while other Next 40 players are working on the subject.
Here’s a look at the ways in which employees can be involved in the company’s success.
BSCPE: Bon de Souscription de Parts de Créateurs d’Entreprise (Business Creators’ Share Subscription Bond)
How BSCPE works
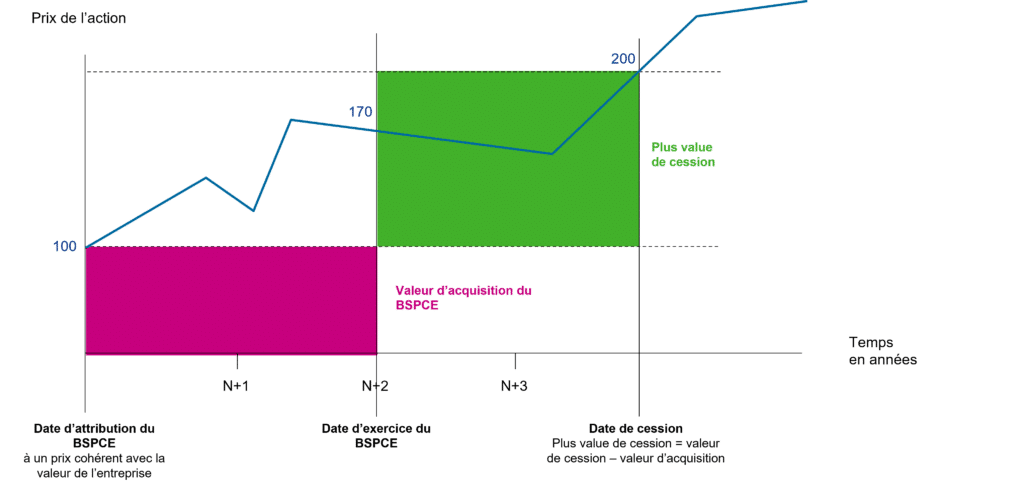
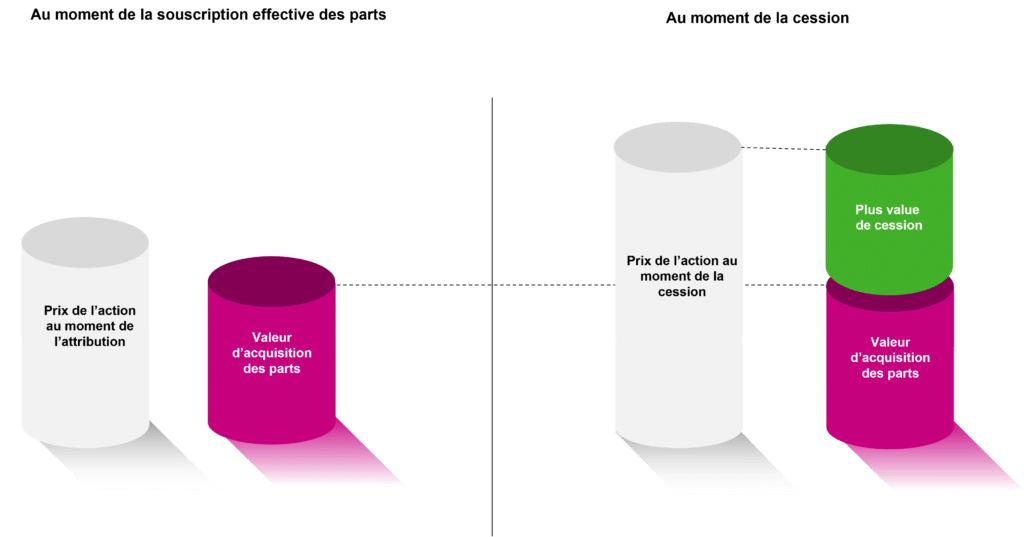
The BSCPE entitles the holder to subscribe to shares in the company at a predetermined price. The beneficiary can decide whether or not to exercise this right.
Vouchers are non-transferable. You need to execute the warrants to become the holder of shares, which are freely transferable in accordance with the company’s articles of association.
Which companies are eligible for BSCPE?
All joint-stock companies are eligible for the BSCPE provided they meet certain conditions:
- Payment of corporate income tax in France
- Market capitalization under €150 million
- Registered less than 15 years ago
- A minimum of 25% of shareholders must be natural persons, or legal entities at least 75% owned by natural persons
Companies resulting from restructuring or takeovers are not eligible.
Who can benefit from the BSCPE?
The BSCPE is only available to salaried employees and managers subject to the salaried employee regime.
BSCPE taxation
Capital gains will be taxed according to length of service with the company:
- More than 3 years: taxable at the PFU rate of 30%, or at the progressive income tax rate
- Less than 3 years: fixed rate of 30% + social security contributions of 17.2%.
AGA: Allocation of free shares
How the AGM works
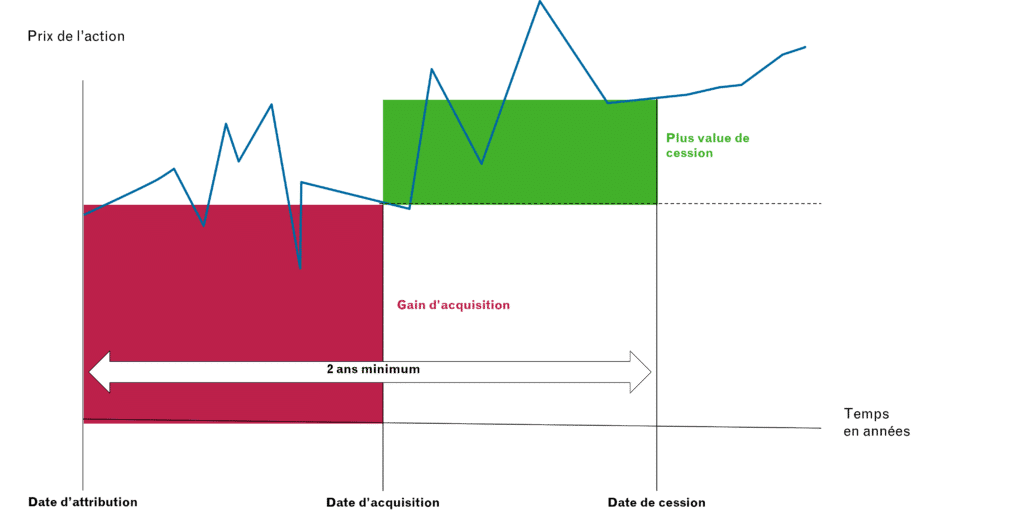
This involves the automatic acquisition of free shares in the company after a vesting period and a minimum 2-year holding period (vesting period + holding period).
The right to a claim begins as soon as the share is allocated, but it does not become transferable until the holding period has expired.
Which companies are eligible for the AGA?
All joint-stock companies, whether listed or not, can distribute free shares.
The allocation of free shares entails payment of an employer’s contribution corresponding to 20% of the value of the shares allocated. It is payable
⚠️ There are exemptions for SMEs that have not distributed dividends and meet the definition of a European SME (< 250 employees and sales < €50m or total assets < €43m).
Who can benefit from the AGA?
All employees and corporate officers are eligible to receive bonus shares, subject to the following conditions:
- Corporate officers may not receive shares if they already hold 10% of the capital, or if the AGM would cause them to exceed this 10% ceiling.
- The total number of AGAs may not exceed 10% of the share capital, or 30% if all employees benefit.
AGA taxation
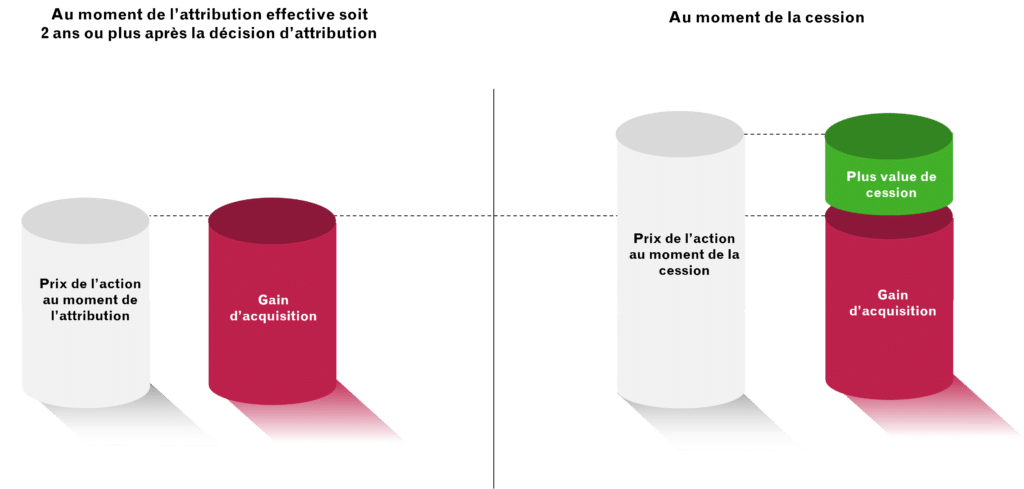
A distinction must be made between 2 elements:
- The gain on acquisition = value of the shares at the date of their definitive acquisition
- The capital gain on the sale of shares = sale price – value of the shares at the date of their final acquisition.
Vesting gains (value at the time of grant) depend on the value of the gain (case of vested shares granted on or after January 1, 2018):
- Fraction under 300,000 euros: 50% allowance, then taxed at IR and 17.2% social security contributions
- Fraction in excess of 300,000 euros: taxable at IR without allowance, social security contributions (CSG and CRDS) of 9.7% and employee contribution at 10%.
⚠️ There are also deductions in the event of retirement or for AGAs carried out in SMEs.
Capital gains (sale price – value at the time of allocation) are subject to the 30% PFU tax, or to the progressive personal income tax scale.
BSA: share subscription warrants
How the BSA works
The BSA entitles the holder to subscribe for shares in the company at a predetermined price. The beneficiary can decide whether or not to exercise this right.
Both the warrants and the shares resulting from their exercise are freely transferable, within the limits set by the company’s bylaws.
Which companies are eligible for the BSA?
All joint-stock companies may issue warrants, regardless of whether they are listed on a regulated market.
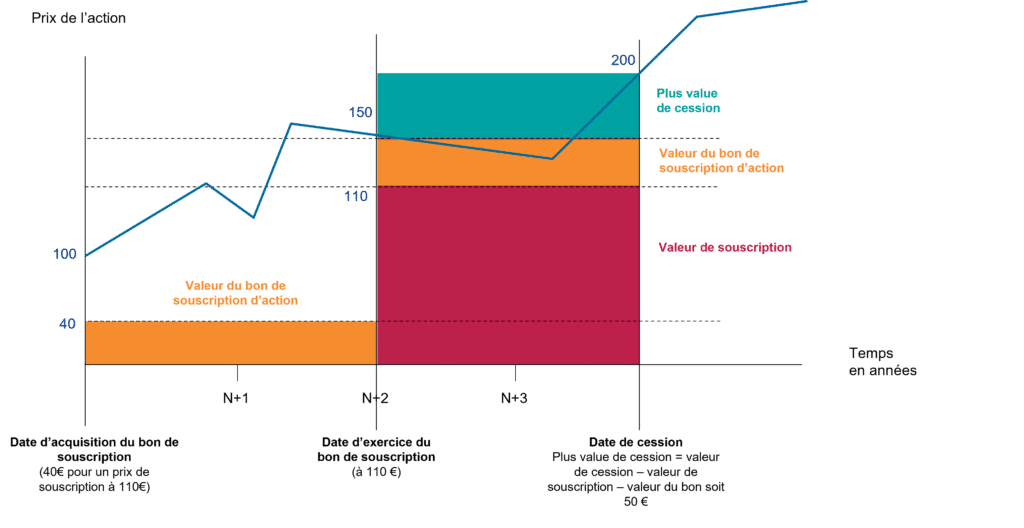
Who can benefit from the BSA?
BSAs may be granted to company employees, corporate officers or third parties.
Taxation of warrants
In the event of disposal, the resulting capital gain is taxable at :
- At the 30% tax rate (12.8% income tax and 17.2% social security contributions)
- Progressive income tax scale
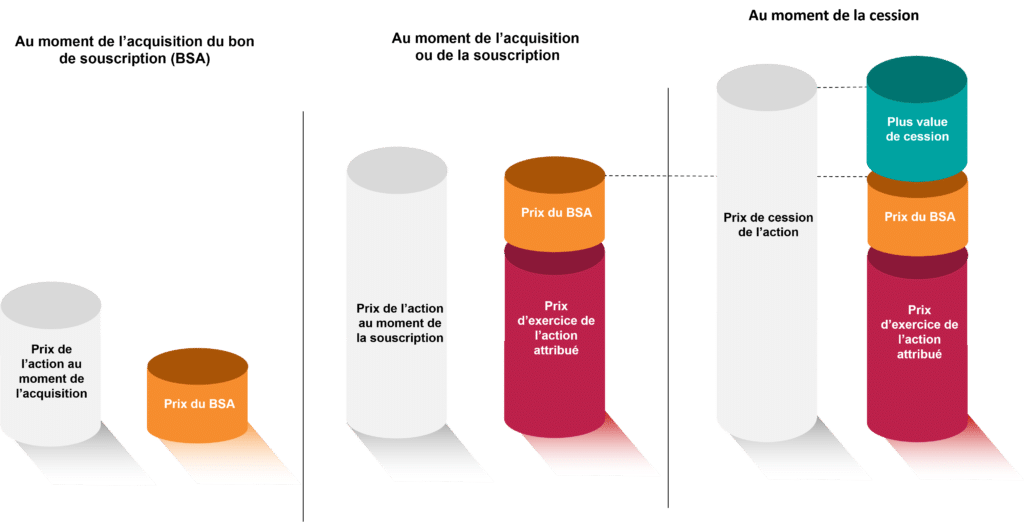
⚠️ If stock warrants are granted at a preferential price compared with their actual value at the acquisition date (e.g. €10 warrants at a subscription price of €50, whereas the share price is €100), the acquisition gain (€40 in the example) may be requalified as wages and salaries.
Stock options
How stock options work
These are options to subscribe for or acquire shares in the company, during a pre-established period, at a pre-established price.
These rights are not transferable until they have been exercised.
Which companies are eligible for stock options?
All joint-stock companies can issue stock options.
Companies are subject to a 30% employer contribution for options granted since July 11, 2012.
Who can benefit from stock options?
All employees of the company, but also employees of separate companies belonging to the same group.
Stock options are also available to corporate officers, provided they do not own more than 10% of the share capital.
Taxation of stock options
Vested shares granted on or after January 1, 2018
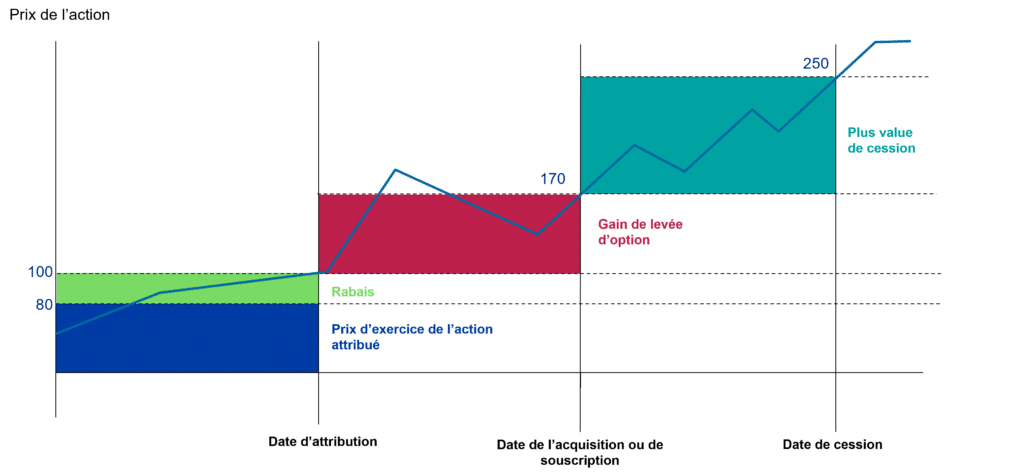
There are 3 stages:
- The time of grant: No taxation at the time of grant but generation of a discount (share price granted at the time of grant – exercise price of the share granted)
- Time of acquisition or subscription: Tax on excess discount at time of subscription. No taxation on the option exercise gain (share price at the time of subscription – share price at the time of grant) at the time of subscription.
- Time of sale / The sale is the triggering event for the option exercise gain, but also for the capital gain on sale (sale price – actual share price at the time of subscription).
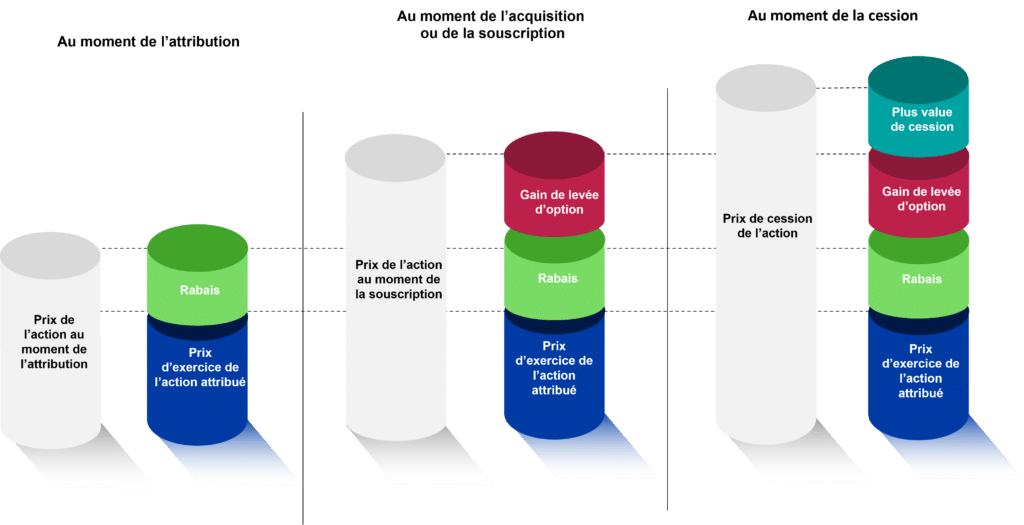
Maximum discount of 20% of share value.
If rebate >> 5% of share value, then creation of an excess rebate for the fraction > > 5%.
Tax exemption on the rebate fraction <= 5%.
If rebate > 5% of the value of the shares => fraction of the excess rebate taxable as salary at the progressive income tax rate for the year in which the option is exercised + social security contributions (9.2% CSG and 0.5% CRDS)
Example: for a share priced at €150, the maximum discount will be €30 and the excess discount will correspond to the fraction between €7.5 and €30.
Option exercise gain (taxed when the share is sold):taxable as salary on the progressive scale of income tax for the year in which the option is exercised + social security contributions (9.2% CSG and 0.5% CRDS).
Gains on disposal (taxed when the share is sold):taxable as capital gains: -either at the PFU rate of 30% -or at the progressive income tax rate + social security contributions at 17.2%.
⚠️ There are different tax treatments for stock options granted before 2018.
👆 Would you like to involve your employees in your company’s success, but don’t know how to go about it? Altermès can help you add value to your business and choose the best solution for your company and your employees.
🔍 Find out how we helped an investment fund value the shares subscribed by exercising BSPCEs on behalf of a fast-growing company!











